When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Here’s how it works.
How to Connect a Second Router Wirelessly – Overview
In this digital age, linking two wireless routers without needing an Ethernet cable has become straightforward. While most Wi-Fi networks utilize a single router, there are several scenarios where adding a second router is beneficial.
For example, suppose you encounter weak Wi-Fi signals at home or in your business. In that case, a second router can extend the Wi-Fi range, ensuring connectivity even in the furthest corners of the area. Identifying Wi-Fi dead zones in your home or business is the first step toward mitigating this issue. Positioning a second router in these spots can significantly improve internet access.
Generally, integrating a second router wirelessly is not overly complex, but there are important considerations. This article outlines the general steps to efficiently add a second router to your existing internet setup.
Before You Proceed
The range of a Wi-Fi router is influenced by the wireless standard it supports. For instance, devices using Wireless N (802.11n) typically offer better range than those with Wireless G (802.11g).
Therefore, using two Wireless N devices is advisable, although a Wireless G device can suffice as a second router. Before starting the setup process, ensure you note the name, passcode, and SSID (service set identifier) of each router.
The placement of the repeater router is crucial. Initially, you may set it up next to your computer, moving it to the identified dead zones upon completion.
The Setup Process
- Begin with your primary router already in place, connect the second router and reset it to factory settings. This reset button, often a small, indented hole labeled “reset” at the back of the router, requires pressing with a pin. Some routers may feature a physical button instead.
- With the router powered on, press and hold the reset button with a pin for several seconds. Releasing the pin should temporarily turn off all router lights before they turn back on, indicating that the router has been reset and is ready for new settings.
- If you encounter issues with the reset process, seek specific troubleshooting steps online.

How to Connect a Second Router Wirelessly
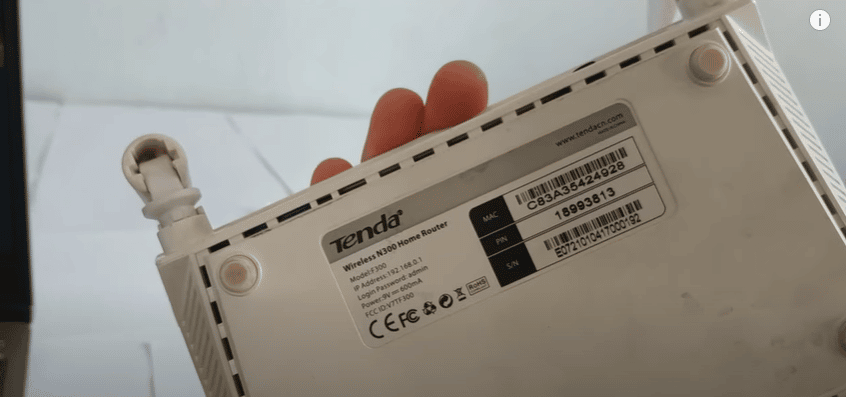
- Now, connect your PC to the Wi-Fi network broadcasted by the second router. Network information is typically found underneath or at the back of the router.
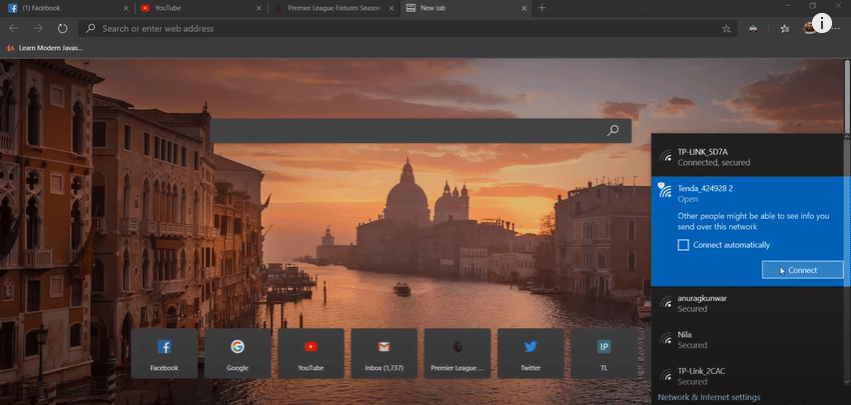
- Access the router’s configuration page using its IP address. The configuration username and password are also indicated at the back of the router.
- Upon accessing the configuration page, bypass any setup wizards and navigate to the Wi-Fi or wireless settings section.
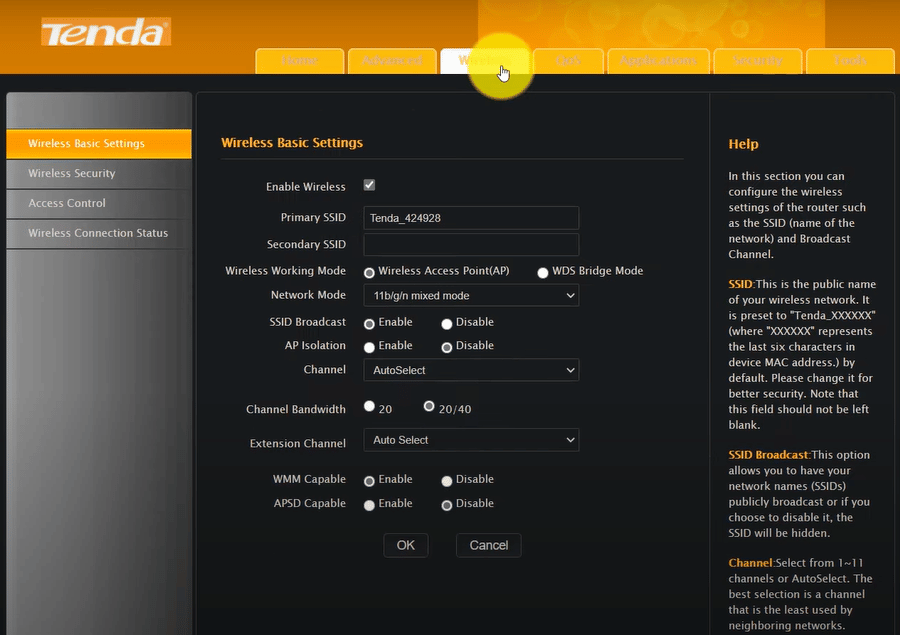
- Modify the network mode from ‘Access Point (AP)’ to ‘Repeater’ mode. Depending on the device, setting up a wireless bridge may be necessary.
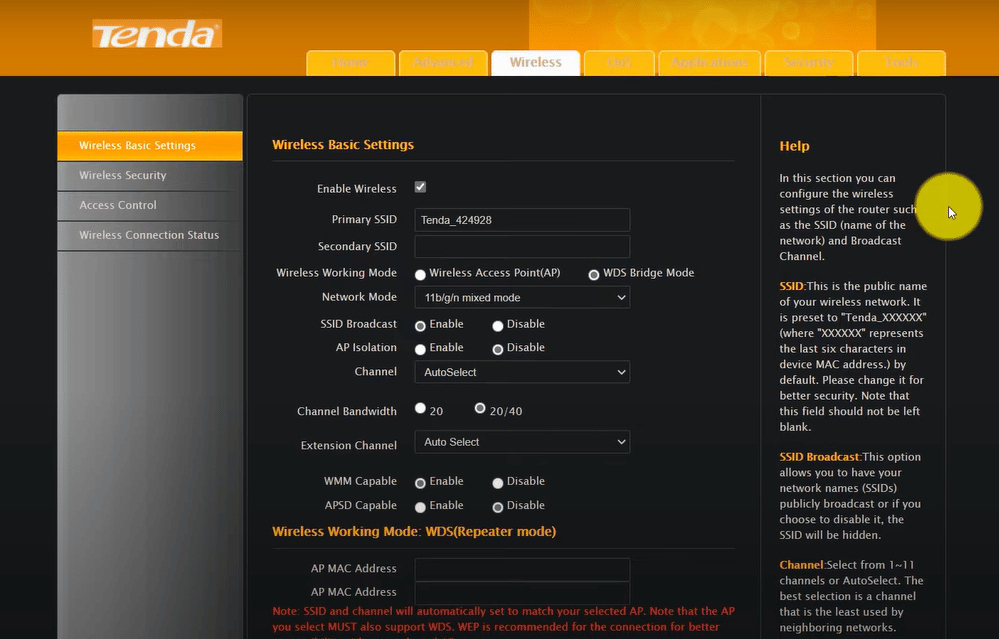
- Adjust the Wi-Fi name to mirror your primary network, yet with slight differentiation, e.g., ‘Home’ becomes ‘Home-Ext’.
- Also, synchronize the Wi-Fi password and security type with your primary network.
- Enter your primary router’s MAC address inthe configuration page.
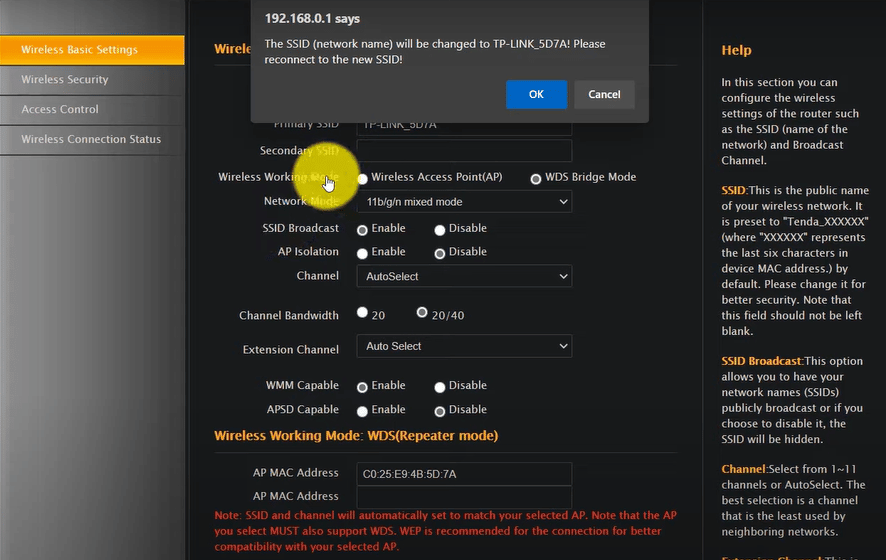
- Examine the LAN/IP address settings. Deactivate any options that would configure the second router as a ‘DHCP Server’ to prevent it from assuming the role of the primary router.
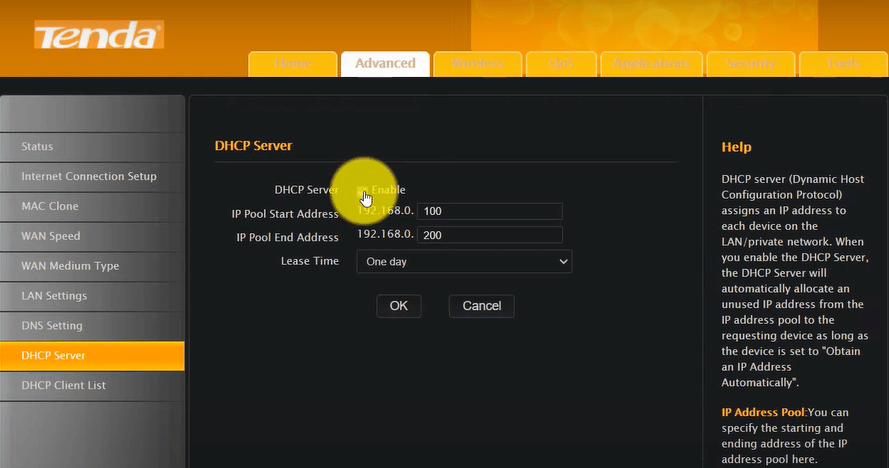
- Verify that the adjustments you’ve made align with your primary router’s settings.
- Save these settings to apply the changes.
- Turn off both routers, wait for a minute, then power on the primary router only.
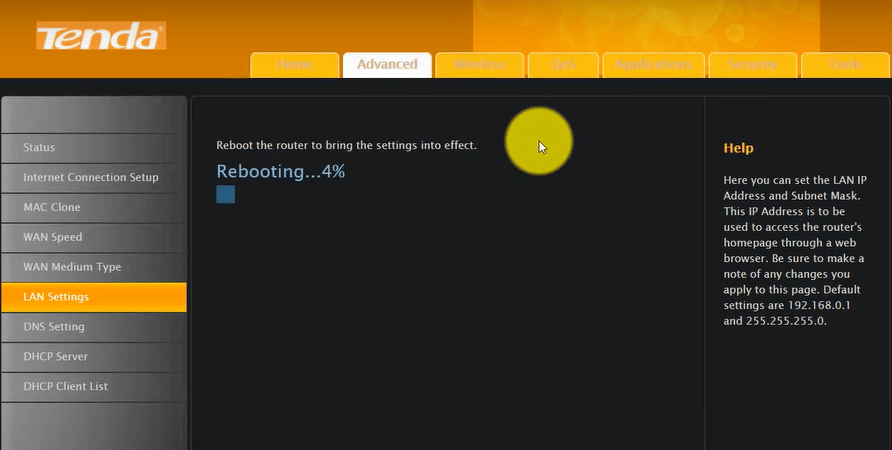
- Subsequently, power on the second router and allow a few seconds for it to connect to the primary router.
- This action signifies that the second router successfully extends the primary router’s signal, establishing an active connection.

- Lastly, connect to the second router’s Wi-Fi using a smartphone, PC, or tablet to test the network strength near the router.
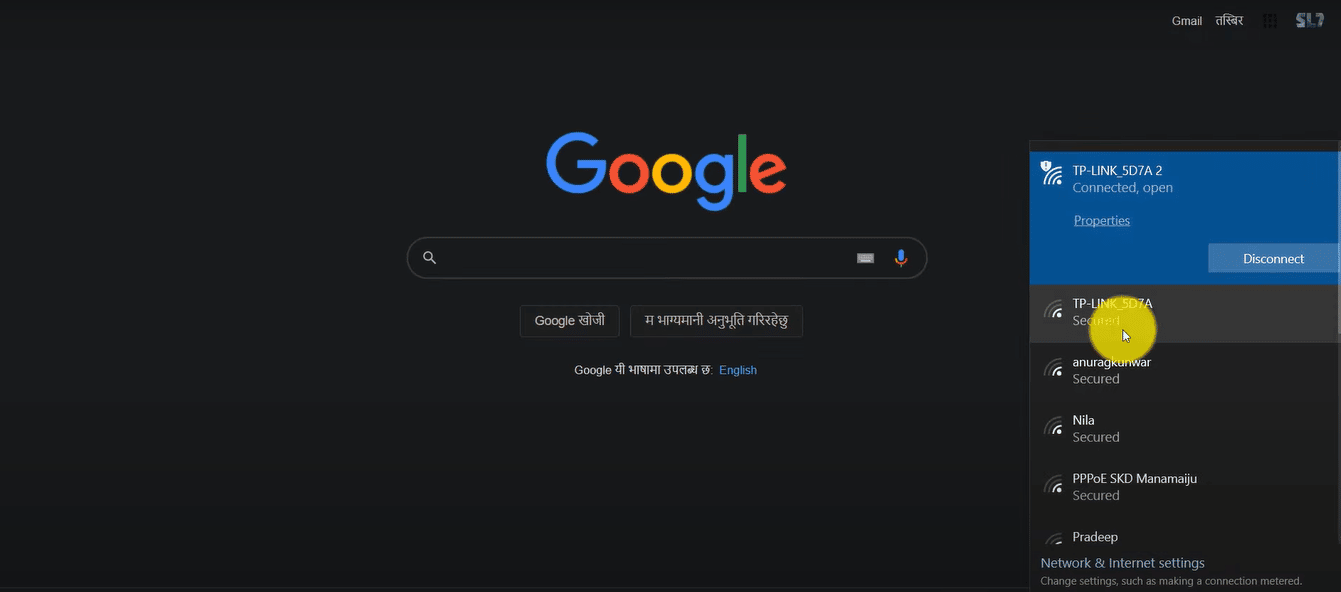
- You have now successfully connected a second router wirelessly to your home network, extending your Wi-Fi range and adding a secondary access point.
How to Connect a Second Router Wirelessly
Note: Wireless connections between routers can face challenges if physical barriers exist. For optimal connectivity, ensure the routers are positioned with minimal obstructions between them.
Final Thought
As demonstrated, connecting a second router wirelessly to your home Wi-Fi network is straightforward and cost-effective. This solution is particularly useful for extending internet coverage to Wi-Fi dead zones. It is especially handy if you have an old Wi-Fi router available for use in your home or office.
See Also
How to Check Browsing History on a Wi-Fi Router
Best Router for Multiple Devices