When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Here’s how it works.
What is Z-Wave? – Overview
Are you searching for reliable and secure communication with a simple installation that consumes low power and is very affordable?
To answer this question you should know, what is Z-Wave? The wireless communication protocol for home automation devices is the technology known as Z-Wave.
In the world of Internet-of-Things (IoT), it is one of the new communication standards. Z-Wave popular communication protocol after Zigbee.
According to the Statista Global Consumer Survey, Smart Home Market Project will result in a revenue of US$104,401M in the 2030s.
Household penetration will be 12.3% in 2021, by 2025 it’s expected to be 21.90%. The average revenue per Smart Home installed device currently is an amount of US$396.44M.
What is Z-Wave?
Z-Wave operates at 900 MHz frequency band, whereas Zigbee protocol works at 24 GHz.
Due to band constraints as per regions, Z-Wave is a geography-specific protocol that consists of different legally permissible frequencies in different localities.
However, Z-Wave prefers a low-frequency region. Long-wavelength and Low frequency establish the faster communication topology among the devices which are connected.
Mesh Network is a source router that Z-Wave uses as the primary node referred to as the controller or hub in home automation and sensors to be the secondary node.
The primary controllers are identified by network IDs and the secondary nodes by Node IDs. Communication is not possible if different network IDs are assigned to devices.
Mesh network technology includes the primary controller that can send messages to Z-Wave devices by making a channel for a signal via intermediate devices in the shortest path possible.
Signal hopping is the name given to the process of signal transfer. Other available paths are selected by the devices if the devices within the path are busy.
Z-Wave Features
- Lower Transmission Power – Z-Wave ensures 3-5 years of battery life to its users with much lower transmission power consumption.
- Frequency Bands – 900MHz frequency bands are required for Z-Wave operations resulting in less interference and higher penetration.
- Interoperability – Interoperability is allowed by Z-Wave among versions through 6 layers of Backward Compatibility.
- Communication – 120 feet to 40 meters is a range of communication with Z-Wave devices.
- Security – Higher security is carried out through AES128 encryption as Z-Wave offers 100 Kbps data rates.
- Interference – Z-wave devices will not interfere with Wifi or any other household signals within the home while working on a different frequency.
- Set-Up – 232 devices are configured within the Z-Wave network.
Difference Between Z-Wave and Z-Wave Plus
| BASIS | Z-WAVE | Z-WAVE PLUS |
|---|---|---|
| Existence | Latest Technology. | Came into Existence in 2013. |
| Range | Extends Communication between devices from 20 feet to 40 meters. | Extended device communication range. |
| Device Size | Large in size requires more power to operate. | Smaller in size and requires less power to operate. |
| Battery Life | 3 to 5 years. | Lasts up to 10 years. |
| Backward Compatibility | It works on Z-Wave classic series 300 and 400. | It works on Z-Wave 500 series that in the future will rise to 700. |
| Connection | Need to look after the network to be connected. | It will automatically connect to the Mesh network. |
| Self Heal | Have to look after the problem that arises in the devices. | It automatically recovers the problem before you even realize there was one. |
| Bandwidth | Able to handle only allowed data. | Able to handle 250% more data than Z-Wave. |
| Channels | Has only I channel. | It has 3 channels. |
Z-Wave Products
What is Z-Wave? Z wave products
How Does Z-Wave Work?
Z-Wave is a wire-free technology that is operated at 908.42MHz (in the US and Canada). Z-Wave comprises smart devices to communicate and connect with other devices.
Z-Wave connectivity is added as a feature in Z-Wave products making them capable to communicate and function as per user desire.
Z-Wave operates securely and wirelessly. The devices are accessible and controllable easily on the smartphone, tablet and computer so users can control them virtually from anywhere in the world.
The Z-Wave hub receives the command of the connected devices and passes it to the destination devices.
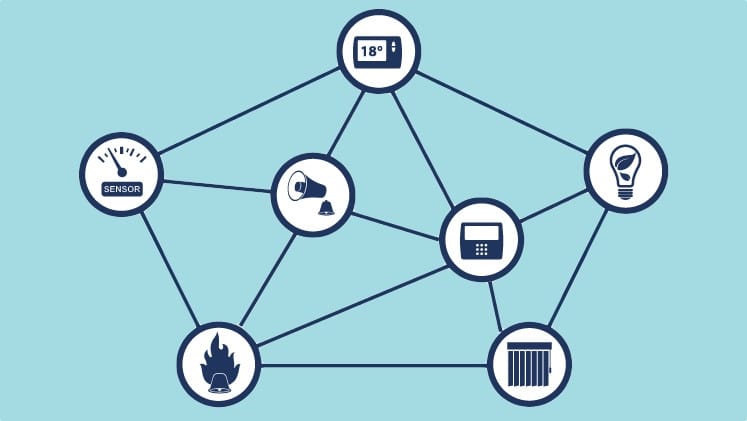
What is Z-Wave? – How does Z Wave work
For Instance, You want to switch off the lights in your room. You have to select the option on your device.
As long as you have access to the internet, no matter where you are, the hub will receive the command which will be forwarded to the lighting solution controller.
Once the lights are off, a notification message will be sent back to the device. Hence, the work is done without any interruption.
Advantages of Z-Wave
- Compatibility – Z-Wave is compatible with other devices as all smart home devices connect and communicate with each other.
- Wirefree – Appliances can communicate within 50-100 feet apart from each other as a connection to the network is maintained without being within the router range.
- Set-up – Z-Wave has an easy set-up installation as it is wireless. Devices can be easily removed and added without router interference leading to the establishment of the home automation system.
- Flexibility – It can easily accommodate changes to varied products.
- Efficiency – It has excellent performance as it is operated at 908.42MHz.
- Suitability – Z-Wave is best for small businesses and residential homes.
- Secure – Z-Wave uses AES-128 encryption to provide a secure network. Z-Wave is more reliable and easy to install.
- Interoperable – It allows users to add or remove the devices giving them total space for a smooth connection.
- Range – Z-Wave experiences enhanced range optimization through the device looping aspect of the technology.
- Transmission Speed – The transmission speed of 9.6 kbps, 40 kbps and 100 kbps data rates are supported by Z-Wave.
Disadvantages of Z-Wave
- Signal Transmission – The connected devices should be within 300sq feet.
- Expensive – The whole setup is quite very expensive due to wireless devices.
- Nodes – Z-Wave is only connected to 232 very limited nodes. Hence, it is only connected to 4 hubs and 4 signals due to connectivity issues.
- Resources – Z-Wave is battery-oriented and consumes power leading to the replacement of batteries more often.
- Security – Hackers can easily hack the system.
- Structure – Only supports a Tree Topology structure.
- Speed – Communication speed is up to 700 Kbps.
Final Thoughts
To sum up, Z-Wave is a smart home technology that is powerful and energy-efficient.
Z-Wave has many advantages over Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. Z-Wave handles the communication by consuming less energy and data.
Moreover, proper security is maintained and accessible to the user from anywhere around the world.
Apart from some pros and cons, this technology is very impactful and can be updated in the future for the betterment of uses.